In this article, you will gain valuable insights into the common symptoms of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in children and the available treatment options. RSV is a highly contagious respiratory infection that primarily affects infants and young children, often leading to serious complications. By understanding the typical symptoms associated with RSV, parents and caregivers can promptly recognize the signs and seek appropriate medical attention. Furthermore, we will explore various treatment modalities that can help alleviate the discomfort caused by RSV and promote the child’s recovery. It is essential to prioritize the health and well-being of our young ones, and this article aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge to do so effectively.
This image is property of my.clevelandclinic.org.
Understanding RSV
What is RSV?
RSV, or Respiratory Syncytial Virus, is a common respiratory infection that affects people of all ages, but is most commonly found in young children. This virus can cause mild cold-like symptoms, but it can also lead to more severe respiratory illness, especially in infants and children with weakened immune systems. RSV is highly contagious and spreads easily from person to person through respiratory droplets, making it a common concern for parents and caregivers.
How is RSV Spread?
RSV is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. These droplets can then be inhaled by others nearby or can contaminate surfaces, where they can survive for several hours. Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the face, mouth, or eyes can also lead to RSV transmission. The virus is most commonly spread during the fall, winter, and early spring months, when respiratory infections are more prevalent.
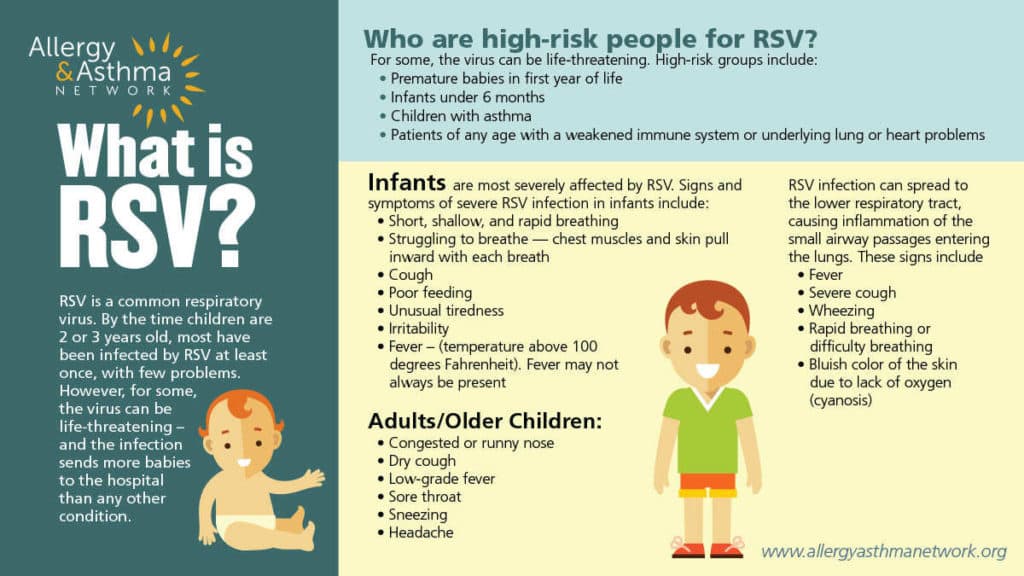
Who is at Risk for RSV?
While RSV can affect people of all ages, certain groups are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms and complications. Infants under the age of 2, especially premature babies, are most susceptible to severe RSV infection. Children with underlying health conditions, such as heart or lung disease, are also more vulnerable. Additionally, young children who attend daycare or have older siblings in school are more likely to come into contact with the virus due to close proximity to others.
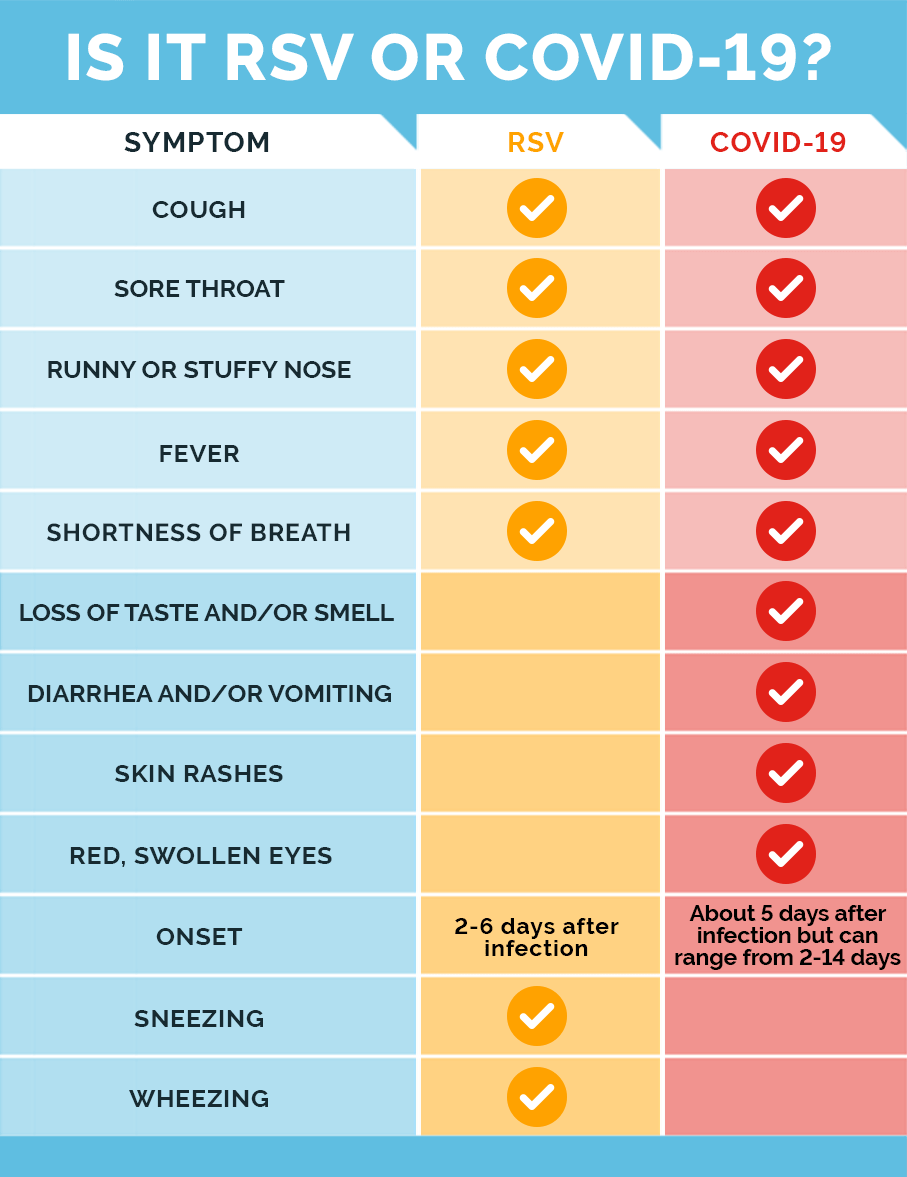
Overview of RSV Symptoms in Kids
General Symptoms
RSV symptoms in children can vary in severity and may resemble those of a common cold. General symptoms of RSV include a runny nose, sneezing, coughing, and a mild fever. These symptoms typically appear within 4-6 days after exposure to the virus.
Early Signs of RSV
Early signs of RSV in children may include irritability, decreased appetite, and difficulty sleeping. These subtle signs are important to recognize, as they can indicate the onset of a respiratory infection. Early intervention and medical attention are crucial in managing RSV and preventing complications.
Severity Levels of RSV Symptoms
RSV symptoms can range from mild to severe. In mild cases, children may have a runny nose, cough, and low-grade fever. However, severe RSV symptoms can include difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, wheezing, and bluish skin color. It is essential to monitor the progression of symptoms and seek medical attention if the child’s respiratory distress worsens.
This image is property of healthmatters.nyp.org.
Specific RSV Symptoms in Infants
Feeding Difficulties
Infants with RSV may experience difficulty feeding due to nasal congestion and respiratory distress. They may have decreased appetite, take shorter feedings, or struggle to suck effectively. It is important to ensure that infants are getting enough fluids and nutrition during this time by working with a healthcare provider to develop a feeding plan.
Irritability
RSV can cause infants to become increasingly irritable. They may be fussy, cry more than usual, and have difficulty being consoled. This irritability is often due to the discomfort caused by respiratory symptoms and overall feeling of being unwell.
Decreased Activity
Infants with RSV may exhibit decreased activity levels. They may be less interested in playtime, have reduced physical movements, and appear more lethargic overall. This decrease in activity is a result of the body’s energy being diverted to fighting off the viral infection.
Breathing Difficulties
One of the most concerning symptoms of RSV in infants is breathing difficulties. This can include rapid or labored breathing, wheezing, retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles with each breath), and shallow breathing. Severe respiratory distress, characterized by difficulty breathing or bluish skin color, requires immediate medical attention.
Specific RSV Symptoms in Older Children
Persistent Cough
In older children, RSV often presents as a persistent cough that can last for weeks. The cough may be dry or productive, and it may worsen during the night or with physical activity. This prolonged cough can be disruptive to a child’s daily activities and may interfere with sleep.
Fever
Fever is a common symptom of RSV in older children. The fever may be low-grade or moderate, typically ranging from 100.4°F to 102°F (38°C to 39°C). It is important to monitor the child’s temperature and provide appropriate fever-reducing medication as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Cold Symptoms including Runny Nose
Like in younger children, older children with RSV may also experience cold-like symptoms. These can include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, and nasal congestion. These symptoms are often milder in older children, but can still cause discomfort and hinder daily activities.

This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
RSV Complications in Kids
RSV and Asthma
Children who have had RSV in infancy are at an increased risk of developing asthma later in life. RSV can cause long-lasting damage to the airways, making them more susceptible to wheezing and asthma symptoms. It is crucial to monitor respiratory health and work with a healthcare professional to manage any potential asthma development.
RSV and Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is a common complication of RSV infection in infants and young children. It causes inflammation and blockage of the small airways in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties. Severe cases of bronchiolitis may require hospitalization and supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids.
RSV and Pneumonia
In some cases, RSV can progress to pneumonia, an infection that causes inflammation of the lungs. Pneumonia can be severe, particularly in young children and those with weakened immune systems. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent complications and promote recovery.
Long-Term Effects of Severe RSV Infections
Severe RSV infections, especially if accompanied by complications such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia, can have long-term effects on a child’s respiratory health. These effects may include recurring breathing difficulties, increased vulnerability to respiratory infections, and potential delays in lung development. Close monitoring and management of respiratory health are necessary to mitigate long-term effects.
When to Seek Medical Attention for RSV
Signs of Severe RSV
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if your child exhibits signs of severe RSV infection. These signs include severe difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, wheezing, bluish skin color, lethargy, dehydration, and significant decrease in oral intake. Prompt medical intervention is necessary to ensure proper evaluation and treatment.
Best Time to Consult a Doctor
If your child has been diagnosed with RSV or is exhibiting symptoms of the infection, it is generally recommended to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and provide guidance on the appropriate course of action.
Emergency Indicators
Certain emergency indicators require immediate medical attention. If your child is struggling to breathe, has significant retractions (pulling in of the chest muscles with each breath), or is exhibiting extreme lethargy, it is important to seek emergency care without delay. These signs may indicate severe respiratory distress and require urgent evaluation and treatment.

This image is property of cdn.baptistjax.com.
Diagnosis of RSV in Kids
How RSV is Detected
RSV infection is commonly diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment, medical history analysis, and laboratory testing. A healthcare professional will evaluate the child’s symptoms, perform a physical examination, and may collect a nasal or throat swab for laboratory testing to confirm the presence of the virus.
Medical History Analysis
An analysis of the child’s medical history is an essential part of diagnosing RSV. The healthcare professional will inquire about the child’s symptoms, the duration of symptoms, recent exposure to sick individuals, and any underlying health conditions that may increase the risk of complications.
Physical Examination Approach
During a physical examination, the healthcare professional will assess the child’s vital signs, breathing patterns, lung sounds, and general appearance. They will also examine the child’s nasal passages, throat, and lungs for signs of inflammation or blockage. These findings, coupled with the clinical assessment and laboratory test results, contribute to an accurate diagnosis of RSV.
Treatment Options for RSV in Kids
Home Remedies for RSV
In mild cases of RSV, treatment can often be managed at home. It is important to ensure that the child gets plenty of rest, stays hydrated, and receives proper nutrition. Using a cool mist humidifier, providing saline nose drops, and monitoring fever can help alleviate symptoms. However, home remedies should always be discussed with a healthcare professional to ensure they are appropriate for the child’s individual situation.
Pharmaceutical Treatment for RSV
In more severe cases of RSV, or when home remedies are not enough to manage symptoms, a healthcare professional may recommend pharmacological interventions. Medications such as bronchodilators or antiviral medications may be prescribed to ease breathing, reduce inflammation, and target the virus’s replication. These medications should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
Hospitalization for Severe RSV
Severe RSV infections, especially when accompanied by complications or significant respiratory distress, may require hospitalization. Hospitalization allows for close monitoring of the child’s condition, administration of oxygen therapy if needed, and provision of intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration. Hospitalization provides a higher level of care, ensuring that the child receives the necessary support and interventions during their recovery.
This image is property of allergyasthmanetwork.org.
Preventing RSV in Kids
Simple Preventative Measures
Taking simple preventative measures can help reduce the risk of RSV transmission. These measures include frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and avoiding exposure to crowded places, especially during peak RSV seasons. Implementing these practices can help minimize the spread of the virus.
Importance of Good Hygiene
Good hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing RSV infections in children. Apart from frequent handwashing, it is important to regularly clean and disinfect commonly touched surfaces, such as toys and doorknobs. Encouraging children to cover their mouths and noses when coughing or sneezing, and using disposable tissues or their elbows, can also help prevent the spread of the virus.
Vaccination Options
While there is no specific vaccine available for RSV, certain groups of high-risk children may be candidates for preventive intervention called palivizumab. This medication is a monthly injection that aims to provide temporary immunity to RSV and reduce the risk of severe infection. The decision to pursue palivizumab should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, taking into consideration the child’s medical history and risk factors.
Living with RSV
Managing RSV at Home
If your child has been diagnosed with RSV, it is important to follow the recommended management plan provided by a healthcare professional. This plan may include maintaining proper hydration, providing adequate rest, monitoring symptoms, and ensuring a clean and comfortable environment for the child. Regular check-ins with a healthcare professional will help track the child’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to their care.
Long-Term Prognosis of RSV
Most children recover from RSV infections without long-term complications. However, severe cases or complications such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia can have lasting effects on the child’s respiratory health. Close monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare professional are crucial to assess the child’s lung function and ensure appropriate management throughout their development.
Support for Parents and Caregivers
Caring for a child with RSV can be challenging and emotionally taxing for parents and caregivers. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, joining support groups, and staying connected with other parents who have gone through similar experiences can provide valuable guidance and reassurance. It is essential for parents and caregivers to prioritize self-care and seek help when needed.
Recurrence of RSV
Having a previous RSV infection does not confer lifelong immunity, and recurrence of RSV can occur. However, the severity of symptoms is typically lessened during subsequent infections. It is important to continue practicing preventative measures, especially if there are younger siblings or other high-risk individuals in the household, to minimize the risk of recurrent infections.
In conclusion, understanding RSV and its symptoms is crucial for parents and caregivers in order to recognize the signs, seek appropriate medical attention, and take necessary preventive measures. By following proper hygiene practices, closely monitoring symptoms, and working closely with healthcare professionals, the impact of RSV on children can be minimized, promoting a healthy recovery and long-term well-being.


